Cancer is a condition where cells in one part of the body grow and reproduce uncontrollably, destroying healthy tissues. There are more than 200 types of cancer and between 40 and 50 percent of people in the US and UK will develop some form during their lifetime. There are many causes of cancer, but there is also much we can do to prevent this disease, including making positive decisions about what we eat.
Which Cancers Are Most Common?
Globally, the most common cancers are:
- Breast
- Colorectal (bowel)
- Prostate
- Skin
- Lung
What Causes Cancer?
Cancer can be caused by exposure to toxic chemicals or cancer-causing infections such as human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis. Lifestyle decisions — such as tobacco and alcohol use, physical inactivity and poor diet — account for around 40 percent of cases.
Cancer and Diet
Research shows that a healthier diet could prevent up to a third of cancers, which means we have an extraordinary amount of power over our current and future health. For lots of people, however, there is some confusion about what that healthy diet should look like. In fact, studies have found that we need to do two simple things to reduce our diet-related cancer risk:
- Eat more vegetables
- Eat fewer animal products (especially meat)
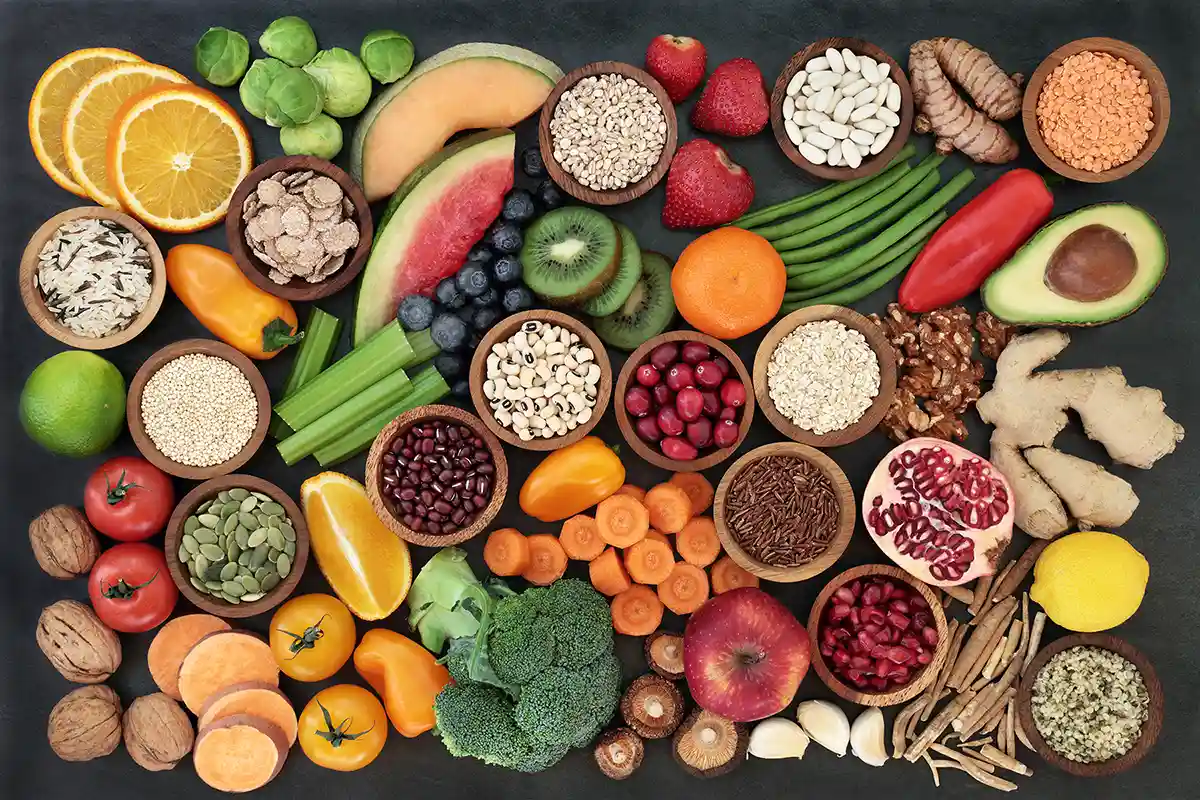

Can Eating Vegetables Prevent Cancer?
Studies show that eating plenty of vegetables, whole grains, and fruits — any foods with lots of fiber — can significantly reduce the risk of some cancers, including colorectal cancer.
“For wholegrains and foods containing dietary fiber the evidence shows that, in general, the more people consume, the lower the risk of some cancers.” — the opinion of the World Cancer Research Fund panel of experts.
In 2017, an estimated 3.9 million deaths worldwide were due to inadequate fruit and vegetable consumption. To get the benefits that plants have to offer, we should consume at least five portions of fruit and vegetables every day. But as we are about to find out, we should not just focus on the cancer-protective foods, we need to look at the foods that actually cause cancer.
Does Meat Cause Cancer?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) there is “convincing evidence” that all processed meats cause cancer. This includes bacon, hot dogs, pastrami, corned beef, chicken nuggets, jerky, and any other meat product that has been processed. The optimal amount of processed meats in our diets is zero.
But it isn’t just processed meat. Red meat is a possible carcinogen too. According to the WHO, evidence shows strong associations between eating red meat and developing colorectal cancer, and there is also evidence of links with pancreatic cancer and prostate cancer. WHO stated that the available data did not permit a conclusion about whether a safe level for eating meat exists.
What about unprocessed chicken and fish? Are they safe? Maybe not. Research found that eating more chicken was associated with a slightly increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma. And interestingly, for fish, a new study has found a link between increased skin cancer and eating non-fried fish. The rate of melanoma was 22 percent higher among people who reported eating the most fish compared with those who ate the least.
So, to reiterate: plants are cancer-protective, and there is no evidence that processed plant foods, such as veggie burgers or vegan fried chicken are associated with cancer, unlike their meat-based counterparts.
The moral of this story? Eat more plants!
Does Dairy Cause Cancer?
That is less certain, as research has produced conflicting results, perhaps because of so many variables, such as whether the cohort studied include people with lactose intolerance, and the kinds of dairy consumed — full-fat, low-fat, processed into cheese etc. However, a number of studies have found a correlation with prostate cancer.
Because the evidence is mixed, the advice often given is to keep consuming dairy products because of the protein and calcium it contains, but you know what else contains lots of lovely calcium and protein, but is cancer-protective? Soy milk.
In fact, this study found that a higher intake of soy was associated with a 10 percent reduced risk of cancer. Soy milk (like other plant milks) is a great alternative to dairy milk for those concerned about their health (or animals, or the environment).

Inflammation and Cancer
Chronic inflammation has been found to affect many different diseases and conditions, including cancer but also cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, pulmonary diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Inflammation is the body’s response to tissue damage caused by physical injury, infection, exposure to toxins, or other types of trauma. Over time, this inflammation can trigger the development and growth of cancerous cells.
While there are many triggers for inflammation, we can adopt an anti-inflammatory diet to reduce the risks. An anti-inflammatory diet excludes ultra-processed foods (such as hot dogs and chicken nuggets), refined grains (such as white rice or pasta), sugary foods, and processed meats. It includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, nuts, beans, and spices like turmeric and ginger. In fact, it looks very much like a whole food plant-based diet.
Best Anti-Cancer Diet
The best anti-cancer diet includes all the principles above: avoid all processed meat, avoid all red meat, avoid all white meat, and avoid fish.
Instead, eat lots of plant-based foods, including plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and the products made from them. And it’s fine to enjoy plant-based convenience foods because processing plants does not cause cancer like processing animals.
If you would like to know more about health and diet, take a look at our more comprehensive Health & Nutrition Guide.
Preventing Cancer
As well as adopting a whole food plant-based diet, there are other steps we can take to significantly reduce our chances of developing cancer. They include not smoking or drinking alcohol, staying physically active, and not getting sunburnt. But eating a whole food plant-based diet is one powerful way to reduce our risks of cancer.